Applications of Game Theory

1. Concept
Game Theory in English is Game Theory.
Game theory is a theoretical framework for understanding social situations (plays) between competing players. In some respects, game theory is the science of strategy, or at least the optimal decision-making of independent and competing agents in a strategic context.
The main pioneers of game theory were the mathematicians John von Neumann and John Nash, as well as the economist Oskar Morgenster. In 1944 John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern wrote and published the book “Game Theory and Economic Behavior”
2. "The Prisoner's Dilemma"
Suppose two kidnappers are caught red-handed, but the FBI has only strong evidence to charge them with a lesser crime. In an effort to find more evidence, the FBI holds the prisoners in separate cells and records their statements in the following way. Each kidnapper is told that (1) if one is guilty, the one who confesses will be set free and the other will be executed, (2) if neither is guilty, both will receive a lighter sentence associated with a lesser crime, and (3) if both are guilty, both will receive a severe punishment that does not include death. Based on payoffs and uncertainty, the predicted solution is that both will confess to kidnapping.
Figure 2.1. The prisoner's dilemma
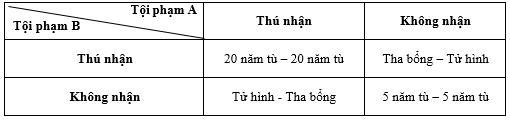
This problem, known as the "Prisoner's Dilemma" , has direct analogues in many types of economic behavior.
Game theory studies how to choose optimal behavior when the costs and benefits of each choice are not fixed, but depend on the choices of other individuals.
3. The impact of game theory on economics
Game theory has revolutionized economics by solving important problems in previous mathematical economic models. For example, neoclassical economics struggled to understand business forecasting and could not explain imperfect competition. Game theory shifted attention away from stable equilibrium to actions within markets.
In business, game theory is useful for modeling competitive behavior among economic agents. Firms often have a number of strategic choices that affect their ability to realize their economic interests.
For example, businesses may face dilemmas such as whether to discontinue existing products or develop new ones, undercut competitors in price, or use new marketing strategies.
Economists often use game theory to understand the behavior of oligopolies. Game theory helps predict the likely outcomes when firms engage in certain behaviors, such as price fixing and collusion.
4. Business behavior in the market
There are four types of market structures: (1) perfectly competitive market; (2) monopolistic competitive market; (3) monopoly market and (4) oligopoly market. Enterprises operating in three types of markets (1,2,3) all follow the principle of MR = MC (marginal profit equals marginal cost) to maximize profits. But in oligopoly markets, each enterprise has a certain power, and at the same time there is strategic interaction (in terms of pricing and output) with other enterprises, so the formula MR = MC is no longer appropriate.
In the perfect competitive market and monopolistic competition, businesses compete with each other to win the market, the level of competition is very fierce in the style of "big fish swallowing small fish". In the oligopoly market, fierce competition will lead to the consequence that businesses all suffer huge losses and damages. It is time for businesses to find a way to compromise, "cooperate" with each other to avoid losses. But cooperation always goes hand in hand with "betrayal", because betrayal brings businesses huge profits. So, between businesses there exists a type of behavior of "both cooperating and competing" with each other. But this situation always contains risks and instability, forcing large businesses to have stable business strategies to ensure their own interests.
The agreement to jointly implement the rules of “general code of conduct – COC” is a wise solution, ensuring that oligopolistic enterprises win in “win-win” business. In fact, we can see the effective business model of the OPEC bloc as a typical example. (The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an organization that ensures stable income for member countries and guarantees oil supplies for customers.)
-Postgraduate Training Institute-










